专四专八好课
经典
专四备考规划
0元
专四水平测试
5分钟
英语专四全程班
特惠
专八备考规划
0元
专八水平测试
5分钟
英语专八全程班
特惠
零基础英语速升
考研好课特惠
介绍
专四专八历年真题
免费
2018英语专业四级必须掌握的语法要点:wish类虚拟语气
英语专业四级语法贯穿于整个英语专业四级考试中,虽说在英语专业四级中考察的题型为语言知识题,20道题,做题时间为10分钟,实则考查内容不只限于语法和词汇这两方面,而是将考查范围扩大到整个语言的运用。
英语语法自我们从小学就开始接触,各类语法内容盘点起来可能能为大家制作成一本英语语法书。其实针对英语专业四级语法复习这八类考点就够了:各类从句、特殊句式、虚拟语气、句意理解、句子成分、非谓语动词、动词时态、情态动词及其他零散的语法知识。其中,其他包括形容词、代词、副词、限定词的用法等。这八类英语专业四级语法考点是怎么得来的呢,我们可以通过往年英语专业四级语法与句型往年真题作为根据。如下图
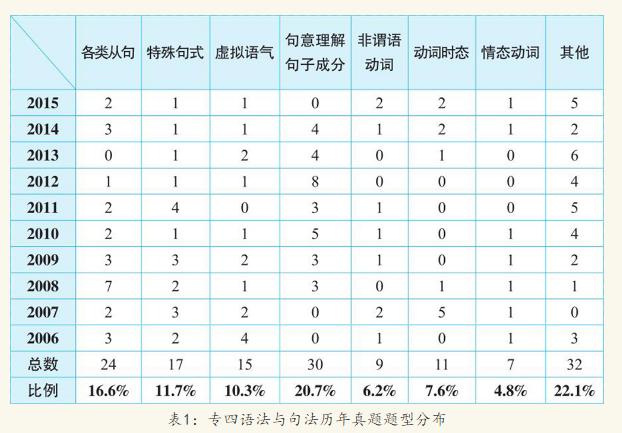
根据对往年英语专业四级真题分析我们可以看出对各类从句的考查比重较大,主要考查名词性从句、定语从句及状语从句。
·对句意理解、句子成分的考查波动较为明显,但总体上比重较大。主要考查对句子意思的理解、句子正误的判断及句子成分的分析。
从上表可以看出,专四语法与句法历年真题的考点主要是各类从句,句意理解、句子成分,特殊句式和虚拟语气,而对动词时态和非谓语动词的考查也占有一定的比重,另外近两年对非谓语动词及动词时态问题也较为重视。
下面我们就逐一为大家讲解英语专业四级八类语法知识点:
1. 非谓语动词的基本用法
·非谓语动词的否定形式:否定词not均加在非谓语动词或者非谓语动词短语的最前面。例如:
Not being tall is not aserious disadvantage in life.
·非谓语动词的时态和语态。
一般说来,动名词和现在分词的一般时表示该动作和主句的动作同时发生,完成时则表示该动作发生在主句动作之前;过去分词的一般时表示该动作发生在主句谓语动词之前,进行时表示该动作和主句动作同时发生;不定式的一般时表示该动作发生在主句动作之后,进行时表示该动作和主句动作同时发生,完成时则表示该动作发生在主句动作之前。
动名词、现在分词和不定式的一般时均表示该动作与其逻辑主语之间为主动关系,如果两者之间是被动关系,则要使用相应的被动形式;过去分词表示该动作与其逻辑主语之间为被动关系。
a)现在分词
一般时:Do you see the man talking to the dean?
一般被动式:You'll find the topic being discussed everywhere.
完成时:Not having made adequate preparations,they failed.
完成被动式:Having been adapted,the script seems perfect.
b)过去分词
一般时:Fight no battle unprepared.
c)不定式
一般时:He decided to work harder.
一般被动式:He preferred to be assigned some heavier work.
进行时:They are said to be holding ameeting now.
完成时:He pretended not to have seen me.
完成被动式:The book is said to have been translated into many languages.
d)动名词
一般时:I enjoy swimming in the big river.
一般被动式:This question is far from being settled.
完成时:I regret not having taken your advice.
完成被动式(通常用一般被动式代替):I still remember being invited/hav
ing been invited by afamous artist when Iwas in Shanghai.
2. 非谓语动词的主要区别
·不定式和动名词作句子的主语、宾语的区别:
a)作主语时,不定式多指具体的、一次性的动作,动名词多泛指概念性动作,在意义上较为笼统和抽象,含普遍意味。例如:
To get there by bike will take us an hour.
Learning from others is important.
b)有些动词要求不定式作宾语,如: afford,agree,aim,apply,arrange,cause,consent,dare,demand,desire,determine,endeavor,expect,fail,hesitate,learn,manage,offer,ought,plan,plot,prepare,presume,pretend,proceed,profess,refuse,resolve,strive,struggle,swear,threaten,tend,volunteer,undertake,wait,want等。
c)有些动词后要求动名词作宾语,如: acknowledge,admit,adore,advise,advocate,anticipate,appreciate,avoid,complete,confess,consider,contemplate,defer,delay,deny,discuss,enjoy,escape,evade,facilitate,fancy,favor,forbid,grudge,imagine,justify,mention,necessitate,postpone,prevent,quit,recall,recommend,renounce,regret,require,resent,resist,resume,risk,stand,suggest,tolerate,warrant等。
d)在can't bear,like,hate,prefer等表示喜好的动词后,动名词表示一般倾向,不定式表示具体行为。例如:
I would like to go with him.
He really loves jogging before breakfast.
e)在bear,deserve,need,require,want等动词后,动名词表示被动含义,不定式表示主动含义。例如:
We want to think it over.
This problem needs thinking about.
f)can not help but,rather than,sooner than,had better,other than短语后接不带to的不定式。例如:
He said he'd sooner die than betray his friend.
g)介词后一般使用动名词作宾语,不用不定式;但是在介词but,except,save后接不定式作宾语,同时,若前面有do anything/nothing/everything结构时,其后接不带to的不定式作宾语。例如:
He wanted nothing but to stay there.
They did nothing but complain.
·现在分词和过去分词作定语、状语的区别。主要考点为:
a)现在分词的一般时表示主动的、正在进行的动作;过去分词的一般时表示被动的、已经完成的动作。分词短语作定语时,逻辑主语为它所修饰的名词;分词短语作状语时,逻辑主语必须和主句主语保持一致。例如:
He stood by the window,reading abook.
There is not much work finished.
c) 表示已经完成的主动的动作,使用现在分词的完成时。例如:
Having finished his homework,Tom went out to meet his friends.
c)表示正在进行的被动的动作,使用现在分词的一般被动式。例如:
This is the question being discussed.
d)表示已经完成的被动动作,既可以用现在分词的完成被动式,也可以用过去分词,但是前者只作状语,不可作定语,而后者作定语、状语均可。例如:
Having been praised asecond time/Praised asecond time,I decided to make still greater progress.
The stolen car was found by the police last week.
e)当分词有独立主语(不同于主句主语的名词或代词)时,则是一种独立主格结构形式。例如:
The bell ringing,we all stopped talking.(=When the bell rang,we all stopped talking.)
There being no bus,we had to walk home.(=There was no bus,so we had to walk home.)
f)现在分词being在独立主格结构中往往被省略。例如:
He came into the room,his face(being)red with cold.
·不定式和分词作句子的定语、状语的区别:
a)动词不定式可以作目的状语,分词不可以。例如:
He got up at6a.m.to catch the earliest train.
b)现在分词可以作结果状语,但是在so...as to...,such...as to...,...enough to...等结构中需用不定式作结果状语。例如:
They all went out,leaving the5-year-old Tom to stay at home alone.
He is not so silly as to do such thing.
c)不定式to find,to see,to learn等通常表示意外的结果,前面可以加上only突出不愉快。例如:
He woke up,only to find himself in adark room.
d)分词短语可以作时间状语和伴随状语,不定式则不可以。例如:
They came out of the classroom,laughing and chatting.(伴随状语)
When asked to speak,he complained about the poor service.(时间状语)
学生党超级福利送上:
新人福利----注册即送150元优惠券:戳图
专四专八:精选好课 暖心助学

 资料下载
资料下载
专八听力训练:时政短语热点【word版】
发布时间:2020-04-01关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八听力】获取
专八翻译模拟练习题总结
发布时间:2020-04-01关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八翻译】获取
专四专八写作必备高级词汇
发布时间:2020-04-01关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八作文】获取
专四听力听写练习50篇文本文档
发布时间:2020-04-01关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专四听力】获取
2021专四写作高级范文15篇集锦
发布时间:2020-04-01关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专四写作】获取
专八基础词汇积累完整版(169页全)
发布时间:2019-12-26关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八词汇】获取
英语专业四级词汇PDF电子版
发布时间:2019-12-26关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专四词汇】获取
近十年专八真题答案及听力原文
发布时间:2019-12-26关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八真题】获取
近十年专四真题答案及听力原文
发布时间:2019-12-26关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专四真题】获取

关注新东方在线服务号
关注新东方在线服务号,
免费获取专四专八必看干货资料

 推荐阅读
推荐阅读
新东方在线专四专八频道给大家整理的相关内容,希望能够对大家的专四专八考试备考有所帮助,更多有关专四专八的备考内容,欢迎随时关注
来源 : 网络 2025-03-18 16:31:00 关键字 : 2025年英语专四常考单词
新东方在线专四专八频道给大家整理的相关内容,希望能够对大家的专四专八考试备考有所帮助,更多有关专四专八的备考内容,欢迎随时关注
来源 : 网络 2025-03-18 16:30:00 关键字 : 英语专四常考单词词源
新东方在线专四专八频道给大家整理的相关内容,希望能够对大家的专四专八考试备考有所帮助,更多有关专四专八的备考内容,欢迎随时关注
来源 : 网络 2025-03-17 16:29:00 关键字 : 2025年英语专四常考单词
新东方在线专四专八频道给大家整理的相关内容,希望能够对大家的专四专八考试备考有所帮助,更多有关专四专八的备考内容,欢迎随时关注
来源 : 网络 2025-03-17 16:28:00 关键字 : 2025年英语专四常考单词
新东方在线专四专八频道给大家整理的相关内容,希望能够对大家的专四专八考试备考有所帮助,更多有关专四专八的备考内容,欢迎随时关注
来源 : 网络 2025-03-16 16:28:00 关键字 : 2025年英语专四常考单词



 精彩课程推荐
精彩课程推荐
直录播结合,知识点精讲,好老师带学,带你稳稳走好备考路
火热报名
直录播精讲互动二合一,新东方好老师全程带学不迷茫!
火热报名
 资料下载
资料下载
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八听力】获取
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八翻译】获取
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八作文】获取
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专四听力】获取
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专四写作】获取
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八词汇】获取
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专四词汇】获取
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专八真题】获取
关注新东方在线服务号
回复【专四真题】获取

 阅读排行榜
阅读排行榜
 相关内容
相关内容